Cell Membrane Structure Journal

With the rapid development of nanotechnology and single-molecule techniques our understanding of cell membranes has substantially increased.
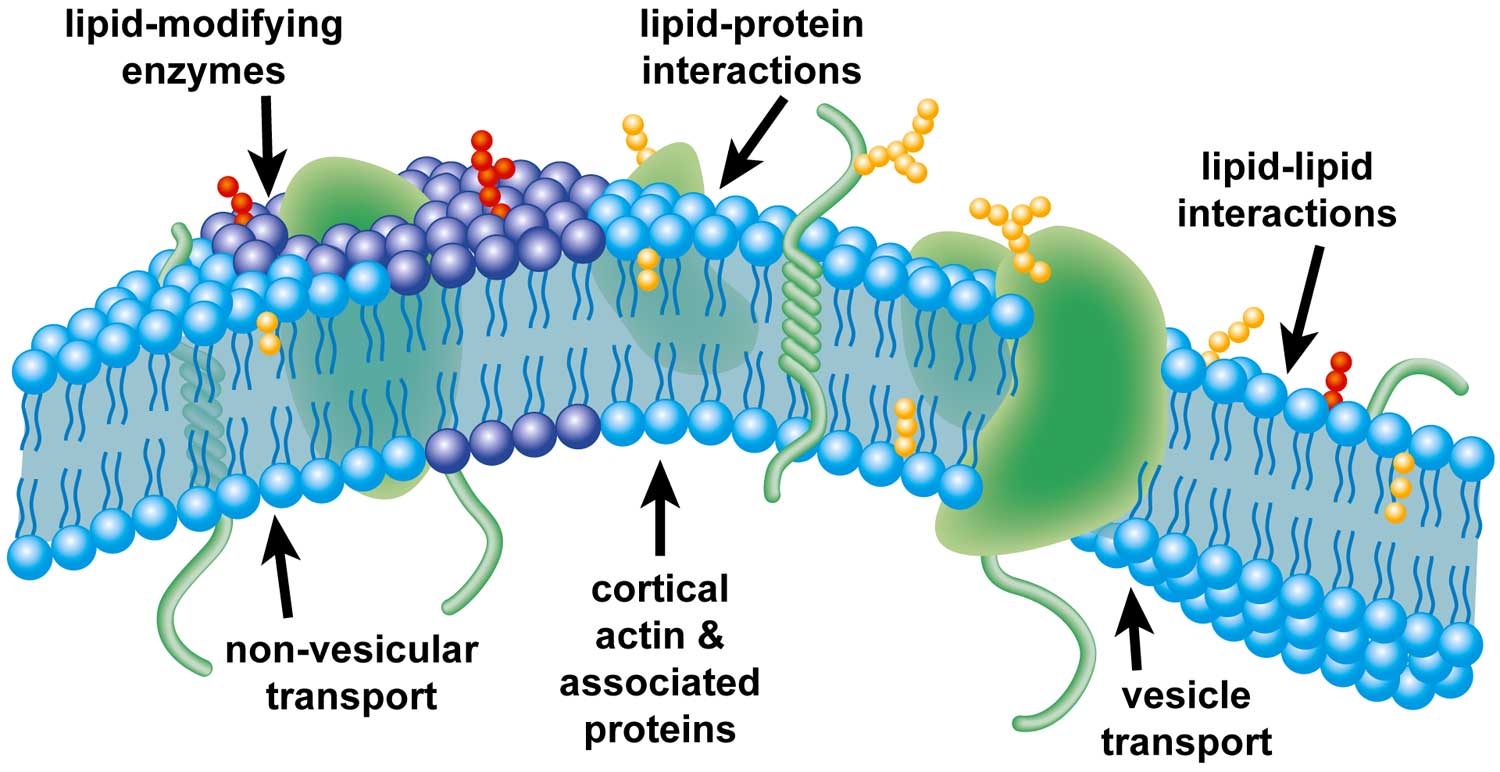
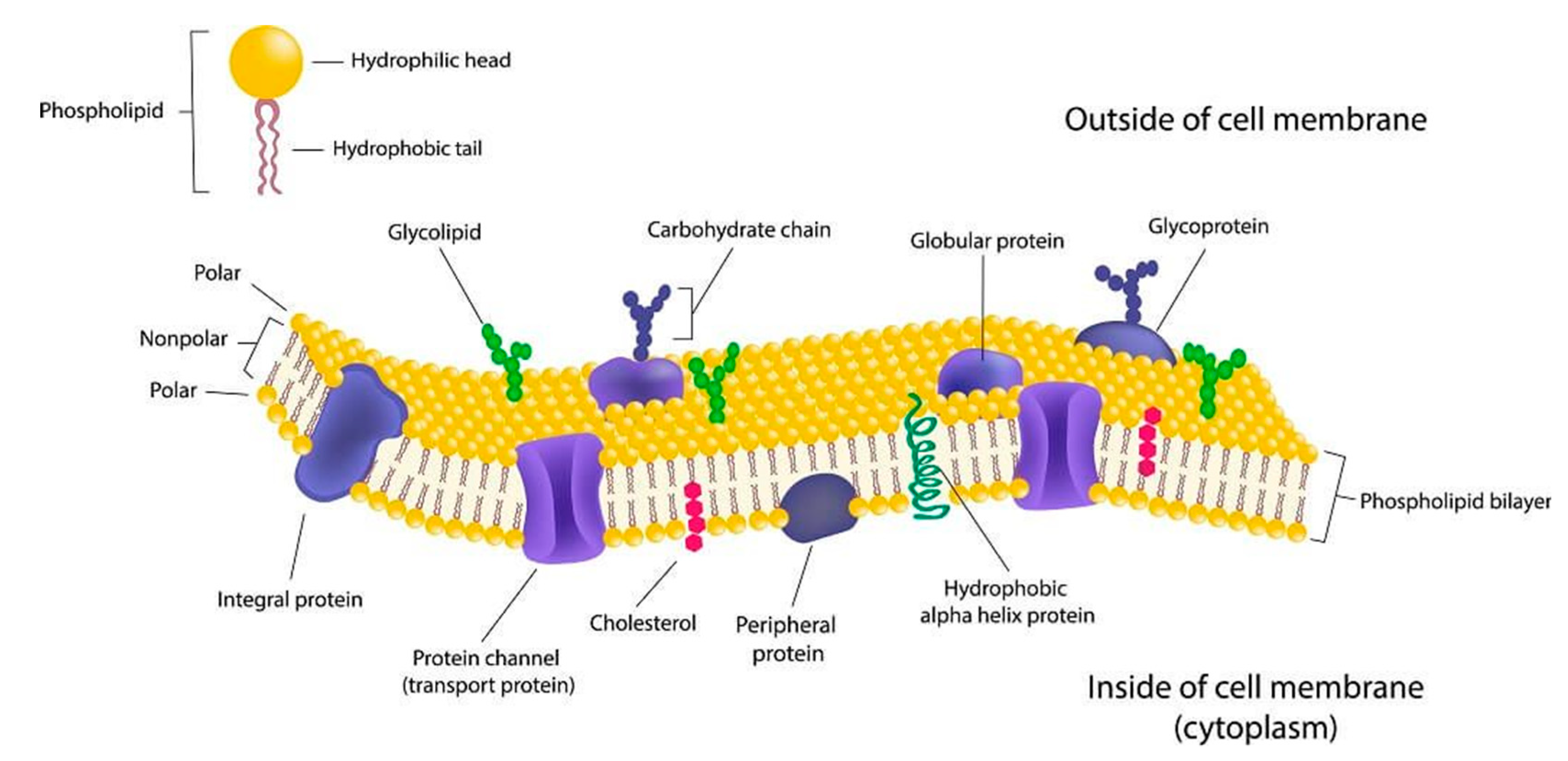
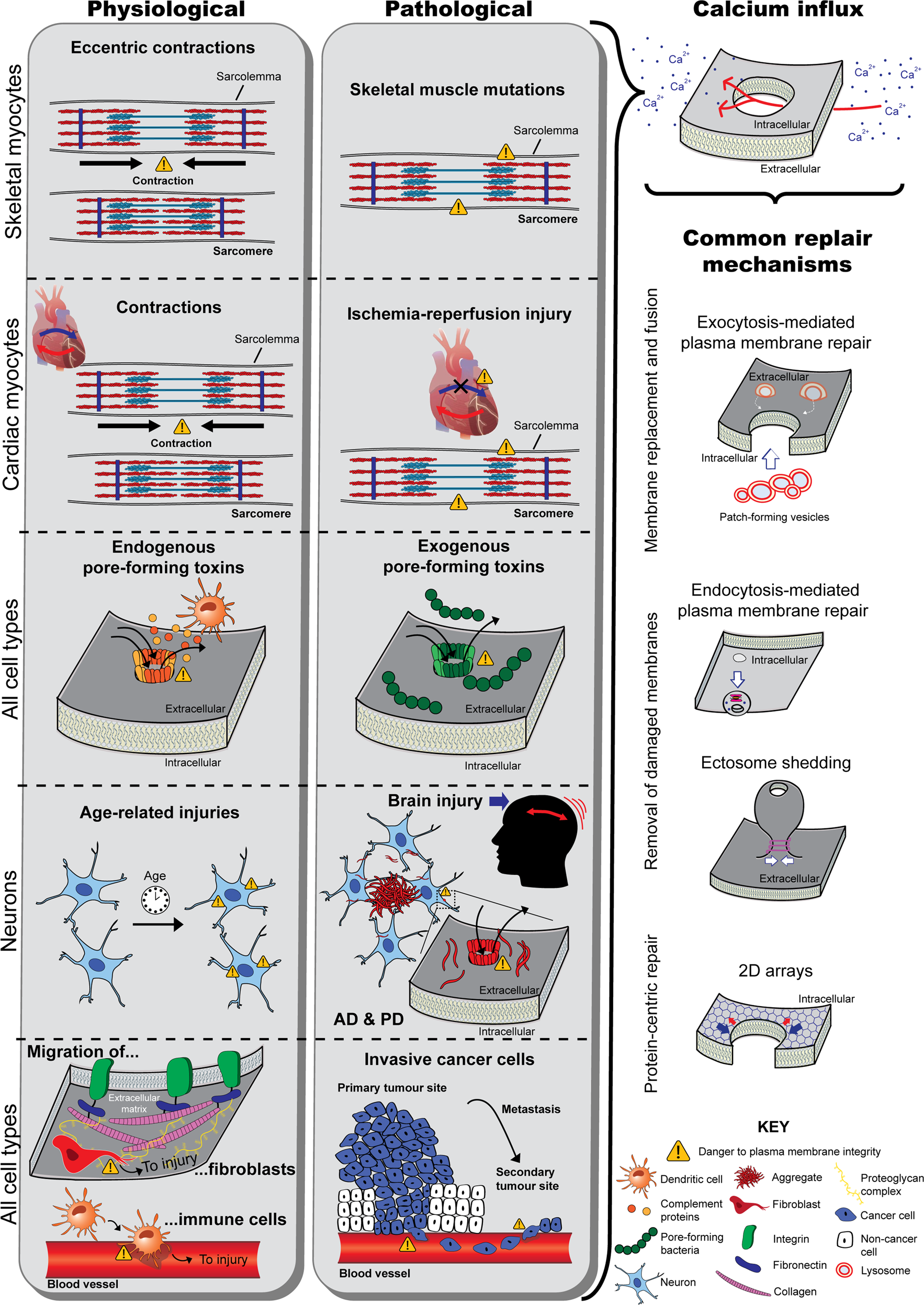
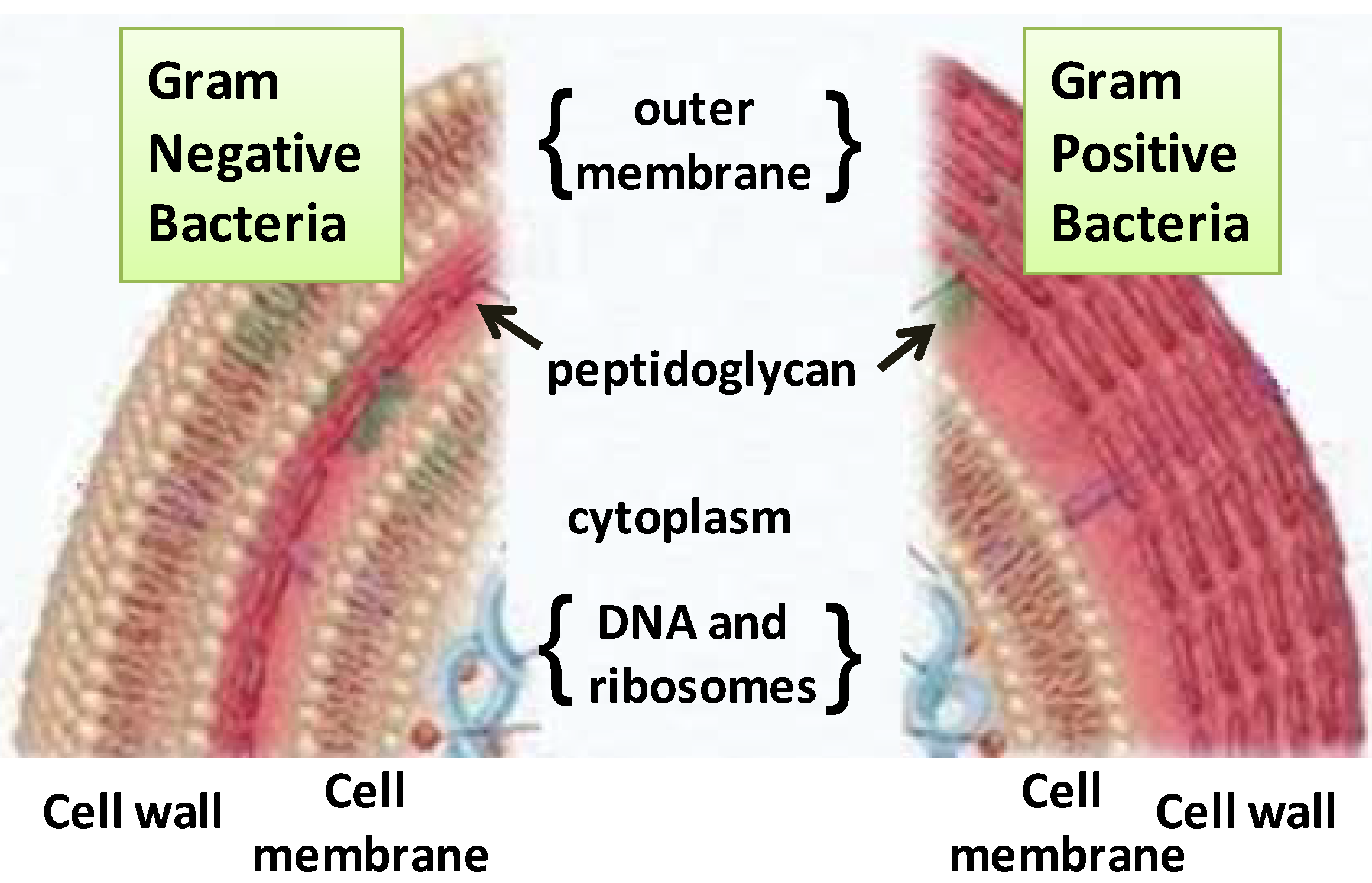
Cell membrane structure journal. Cell membranes are dynamic structures composed of lipid bilayers and integral membrane proteins. These proteins have transmembrane domains which insert into the lipid bilayer and can form complexes with both extracellular and intracellular proteins. For the same token a bacterial toxin does not insert into the membrane through a nonlamellar phase nor two membranes fuse via a rhombohedral phase.
Thefluid mosaic model ofthe cell membrane. Original Research Cell membranes are commonly considered fundamental structures having multiple roles such as confinement storage of lipids sustain and control of membrane proteins. The cell membrane is a complex barrier separating every cell from its external environment.
Introduction The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the intracellular environment from. Considerable progress has been made in understanding the roles played by two membrane lipids. Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals.
3 cholesterol-enriched domains exist in the cell membrane. In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. In particular we welcome work that uses modern experimental or computational methods including but not limited to those with microscopy diffraction NMR computer simulations or biochemistry aimed at membrane associated or membrane embedded proteins or model membrane.
3 in Singer S. Alexa Fluor Dye Conjugates. The cell membrane plasma membrane is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell.
The cell membrane is one of the most complicated biological complexes and long-term fierce debates regarding the cell membrane persist because of technical hurdles. View our cryo-EM collection from Structure and Molecular Cell The papers included in the collection showcase how cryo-EM has enabled us to address SARS-CoV-2 biology antimicrobial resistance mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis the architecture and dynamics of integrator complexes ion channels receptors and phage-genome degradation versus host-genome protection. The paucimolecular unit membrane model of the structure of the plasma membrane is critically reviewed in relation to current knowledge of the chemical and enzymatic composition of isolated plasma membranes the properties of phospholipids the chemistry of fixation for electron microscopy the conformation of membrane proteins the nature of the lipid-protein bonds in membranes and possible mechanisms of transmembrane transport and membrane.