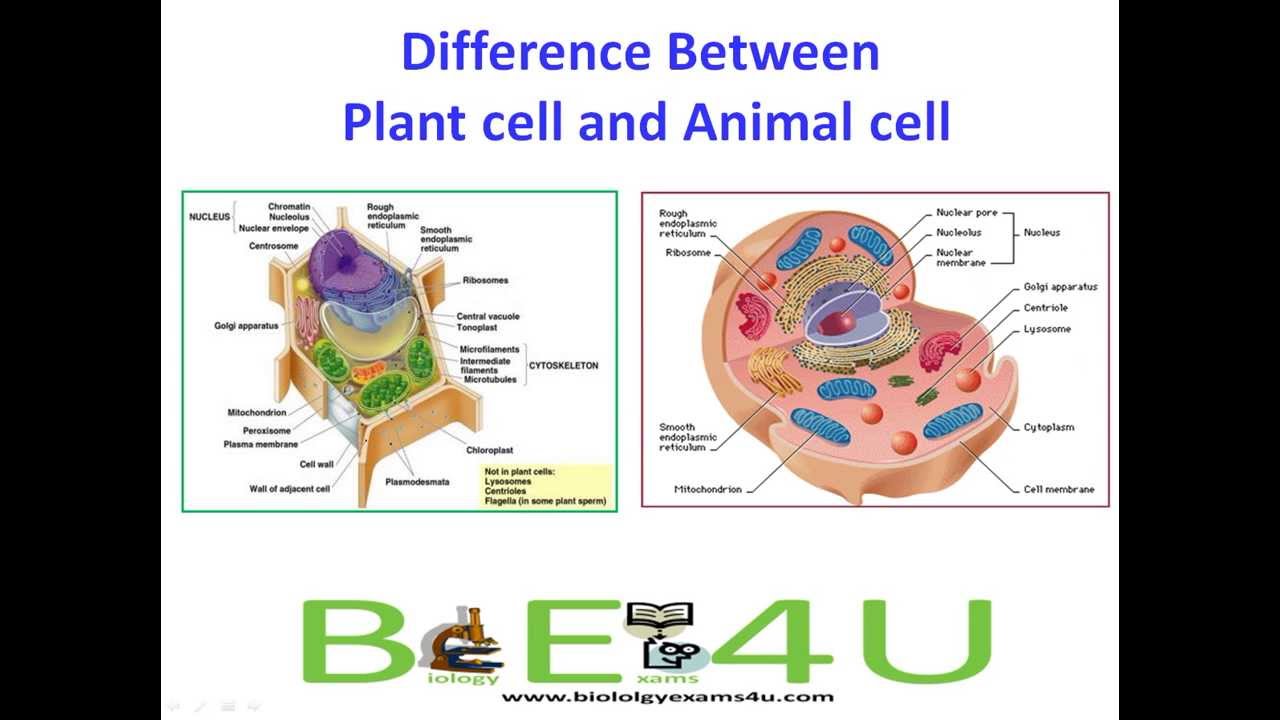
Plants And Animals Difference

If playback doesnt begin shortly try.
Plants and animals difference. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that belong to the kingdom Plantae. It plays a vital role in all biological activities and includes membrane-bound organelles which are involved in various specialized individual functions to keep the cell alive and active. Cell structure and organelles vary in plants and animals and they are primarily classified based on their function.
Plants contain chlorophyll and can. A juvenile stage with distinct may be present in the life-history of a plant. Growth is by addition of new parts ahead or around the older ones.
In an ecosystem plants have the role of producers while animals have taken the role of consumers. A plant cell partitions its cellular material equally between the two identical cells through the formation of concentric contractile microfilament ring. These can be used as the basis for listing similarities between plants and ani-mals.
Plants and animals use various ways to get rid of the waste materials from their body. SIMILARITIES BETWEEN PLANTS AND ANIMALS The plant and animal kingdoms are very diverse yet all living organisms share similar needs and functions. The differences between plants and animals begin at the cellular level and come to include aspects such as mobility.
Plants and animals must avoid becoming a free meal to microbes which vastly outnumber eukaryotic life in both quantity and diversity. Plants generally are rooted in one place and do not move on their own locomotion whereas most animals have the ability to move fairly freely. Green plants have cellulose cell walls and obtain much of their energy from sunlight through the process of photosynthesis.
Difference between Plant and Animal. One difference between plants and animals is that plants do not consist of the digestive system while animals do. In animals there are no passages for that.